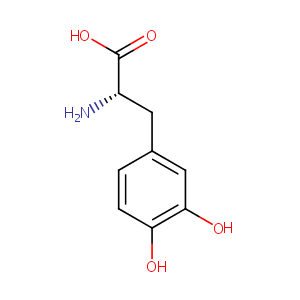
| 1 |
URL: http://www.guidetopharmacology.org Nucleic Acids Res. 2015 Oct 12. pii: gkv1037. The IUPHAR/BPS Guide to PHARMACOLOGY in 2016: towards curated quantitative interactions between 1300 protein targets and 6000 ligands. (Ligand id: 3639).
|
| 2 |
Levodopa FDA Label
|
| 3 |
Determination of anethole trithione in human plasma using high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometric detection. Anal Chim Acta. 2007 Jul 2;594(2):274-8. doi: 10.1016/j.aca.2007.05.038. Epub 2007 May 26.
|
| 4 |
BDDCS applied to over 900 drugs
|
| 5 |
Robertson DR, Wood ND, Everest H, Monks K, Waller DG, Renwick AG, George CF: The effect of age on the pharmacokinetics of levodopa administered alone and in the presence of carbidopa. Br J Clin Pharmacol. 1989 Jul;28(1):61-9.
|
| 6 |
Abrams WB, Coutinho CB, Leon AS, Spiegel HE: Absorption and metabolism of levodopa. JAMA. 1971 Dec 27;218(13):1912-4.
|
| 7 |
Lee CR, Bryson HM: Lacidipine. A review of its pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic properties and therapeutic potential in the treatment of hypertension. Drugs. 1994 Aug;48(2):274-96.
|
| 8 |
Estimating the safe starting dose in phase I clinical trials and no observed effect level based on QSAR modeling of the human maximum recommended daily dose
|
| 9 |
Trend Analysis of a Database of Intravenous Pharmacokinetic Parameters in Humans for 1352 Drug Compounds
|
| 10 |
ADReCS-Target: target profiles for aiding drug safety research and application. Nucleic Acids Res. 2018 Jan 4;46(D1):D911-D917. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkx899.
|
| 11 |
Modulation of LAT1 (SLC7A5) transporter activity and stability by membrane cholesterol. Sci Rep. 2017 Mar 8;7:43580.
|
| 12 |
Human intestinal transporter database: QSAR modeling and virtual profiling of drug uptake, efflux and interactions. Pharm Res. 2013 Apr;30(4):996-1007.
|
| 13 |
Multiple cytochrome P450 enzymes responsible for the oxidative metabolism of the substituted (S)-3-phenylpiperidine, (S,S)-3-[3-(methylsulfonyl)phenyl]-1-propylpiperidine hydrochloride, in human liver microsomes. Drug Metab Dispos. 2002 Dec;30(12):1372-7.
|
| 14 |
Complexity of dopamine metabolism. Cell Commun Signal. 2013 May 17;11(1):34.
|
| 15 |
Reduced 3-O-methyl-dopa levels in OCD patients and their unaffected parents is associated with the low activity M158 COMT allele. Am J Med Genet B Neuropsychiatr Genet. 2010 Mar 5;153B(2):542-548.
|
| 16 |
Discovery and inhibition of an interspecies gut bacterial pathway for Levodopa metabolism. Science. 2019 Jun 14;364(6445). pii: eaau6323.
|
| 17 |
Gut bacterial tyrosine decarboxylases restrict levels of levodopa in the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Nat Commun. 2019 Jan 18;10(1):310.
|
| 18 |
Focal striatal dopamine may potentiate dyskinesias in parkinsonian monkeys. Exp Neurol. 2006 Feb;197(2):363-72. doi: 10.1016/j.expneurol.2005.10.022. Epub 2005 Dec 9.
|
| 19 |
Levodopa activates apoptosis signaling kinase 1 (ASK1) and promotes apoptosis in a neuronal model: implications for the treatment of Parkinson's disease. Chem Res Toxicol. 2011 Oct 17;24(10):1644-52. doi: 10.1021/tx200082h. Epub 2011 Aug 22.
|
| 20 |
Molecular mechanisms controlling the rate and specificity of catechol O-methylation by human soluble catechol O-methyltransferase. Mol Pharmacol. 2001 Feb;59(2):393-402. doi: 10.1124/mol.59.2.393.
|
| 21 |
Plasma dopamine beta hydroxylase (D.B.H.) activity in Parkinsonian patients under L-dopa, and 2-bromo-alpha-ergocriptine loading. J Neural Transm. 1979;46(1):71-8. doi: 10.1007/BF01243430.
|
| 22 |
Association of common genetic variants of HOMER1 gene with levodopa adverse effects in Parkinson's disease patients. Pharmacogenomics J. 2014 Jun;14(3):289-94. doi: 10.1038/tpj.2013.37. Epub 2013 Oct 15.
|
| 23 |
Multiple treatments with L-3,4-dihydroxyphenylalanine modulate dopamine biosynthesis and neurotoxicity through the protein kinase A-transient extracellular signal-regulated kinase and exchange protein activation by cyclic AMP-sustained extracellular signal-regulated kinase signaling pathways. J Neurosci Res. 2014 Dec;92(12):1746-56. doi: 10.1002/jnr.23450. Epub 2014 Jul 12.
|
| 24 |
Dingemanse J, Jorga K, Zurcher G, Schmitt M, Sedek G, Da Prada M, Van Brummelen P "Pharmacokinetic-pharmacodynamic interaction between the COMT inhibitor tolcapone and single-dose levodopa." Br J Clin Pharmacol 40 (1995): 253-62. [PMID: 8527287]
|
| 25 |
Product Information. Azilect (rasagiline). Teva Pharmaceuticals USA, North Wales, PA.
|
| 26 |
Fermaglich J, O'Dougherty DS "Effect of gastric motility on levodopa." Dis Nerv Syst 33 (1972): 624-5. [PMID: 4649158]
|
| 27 |
Ban TA "Drug interactions with psychoactive drugs." Dis Nerv Syst 36 (1975): 164-6. [PMID: 1116424]
|
| 28 |
Therapeutic Research Faculty "Natural Medicines Comprehensive Database.".
|
| 29 |
Mims RB, Scott CL, Modebe O, Bethune JE "Inhibition of L-dopa-induced growth hormone stimulation by pyridoxine and chlorpromazine." J Clin Endocrinol Metab 40 (1975): 256-9. [PMID: 1117978]
|
| 30 |
Morgan JP, Rivera-Calimlim L, Messiha F, Sundaresan PR, Trabert N "Imipramine-mediated interference with levodopa absorption from the gastrointestinal tract in man." Neurology 25 (1975): 1029-34. [PMID: 1237820]
|
| 31 |
Cerner Multum, Inc. "Australian Product Information.".
|
| 32 |
Algeri S, Cerletti C, Curcio M, et al. "Effect of anticholinergic drugs on gastro-intestinal absorption of L-dopa in rats and man." Eur J Pharmacol 35 (1976): 293-9. [PMID: 1248506]
|
| 33 |
Product Information. Nitoman (tetrabenazine). Cambridge Laboratories Ltd, Wallsend, Tyne & Wear, .
|
| 34 |
Carrion C, Espinosa E, Herrero A, Garcia B "Possible vincristine-isoniazid interaction." Ann Pharmacother 29 (1995): 201. [PMID: 7756727]
|
| 35 |
Campbell NR, Hasinoff B "Ferrous sulfate reduces levodopa bioavailability: chelation as a possible mechanism." Clin Pharmacol Ther 45 (1989): 220-5. [PMID: 2920496]
|
| 36 |
Product Information. Zulresso (brexanolone). Sage Therapeutics, Inc., Cambridge, MA.
|
| 37 |
Product Information. Reyvow (lasmiditan). Lilly, Eli and Company, Indianapolis, IN.
|
| 38 |
Product Information. Addyi (flibanserin). Sprout Pharmaceuticals, Raleigh, NC.
|
| 39 |
Product Information. Norprolac (quinagolide). Ferring Inc, North York, IA.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|